Leader in 3D Printing Services
Upload your CAD file for instant quotes across SLA, SLS, FDM, and MJF 3D printing and get overnight delivery. Join 4,600+ engineers who trust us.
Your CAD uploads are protected as per ISO/IEC 27001
Our 3D Printing Services
Experience India's widest and largest 3D printing services, with free online instant quotations.
SLA 3D Printing Services
SLA - Stereolithography
SLA 3D printing offers fast and precise parts with smooth surface finishes and exceptional detail, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and showcase models.
Materials: ABS, Clear PC-Like
Max Print Size: up to 1200mm
Delivery within 24 Hours

SLS 3D PRINTING SERVICES
SLS - Selective Laser Sintering
SLS 3D printing delivers nylon-grade parts, making it ideal for rapid prototyping, end-use functional models and low-batch production.
Materials: Nylon PA12, PA12 + Glass Filled
Max Print Size: up to 450mm
Delivery within 3 days

DLP 3D PRINTING SERVICES
DLP - Digital Light Processing
When design becomes challenging, 3D Systems Figure 4 delivers ultra-thin production grade parts within hours.
Materials: Pro-Black 10, Rubber65A
Max Print Size: up to 200mm
Delivery within hours

FDM 3D PRINTING SERVICE
FDM - Fused Deposition Modeling
FDM 3D printing offers economical prototyping producing strong, durable parts using a variety of filament materials.
Materias: PLA, ABS, TPU, PETG, PC
Max Print Size: up to 500mm
Same day delivery

HP MJF 3D PRINTING SERVICES
HP MJF - Multi Jet Fusion
MJF delivers nylon PA12 end-use parts, which are bio-compatible and well suited for functional rapid prototyping.
Materials: PA12 Nylon (Greyish Black)
Max Print Size: up to 250mm
Delivery within 3 days

3D Scanning & Product Design
3D Scanning & Modeling
Our expert CAD engineers turn your concepts into precise, production‑ready designs—bringing your ideas to life with accuracy and speed.
Simple Part Modifications
Designing products from concepts
Reverse Engineering Services (3D Scanning)

Painting and Finishing
In-house Post Process
Get exceptional finishes and precise RAL color matching, ensuring your parts look exactly as you imagined.
Automotive grade paint booth facility
Finishes: Matte, Glossy, SoftTouch
Delivery within 48 Hours

Industry-Focused 3D Printing Solutions
Customized 3D printing services for automotive, aerospace, defense, healthcare, and more.

EV Battery Management System
EV Automotive

EV Charging Stations
Interior and Exterior Components

EV Cell Holder 3D Printing
2W/4W Automotive

Assembly Jigs & Assembly
Automotive & Robotics

Nylon SLS 3D Printing Services
Aerospace & Defense

Aerospace & Defense
Representation Model

Unmanned UAV 3D Printing
Aerospace & Defense

Canopies, Rubber Pads
Aerospace & Defence

Bio-Compatible Enclosures
Healthcare & Medical

Anatomical models for surgical planning
Healthcare & Medical

Bio Surgical guides
Healthcare & Medical

Industrial Grade Jigs & Fixture
Manufacturing & Tooling

Low Batch Production
Manufacturing & Tooling

Rapid Prototyping
Manufacturing & Tooling

Custom insoles and midsoles
Footwear

Toys & Action Figures 3D Printing
Consumer Products

Customized Home Decor
Consumer Products

Scale models of buildings
Architecture & Construction

Props, Sets and costumes
Film & Entertainment

EV Battery Management System
EV Automotive

EV Charging Stations
Interior and Exterior Components

EV Cell Holder 3D Printing
2W/4W Automotive

Assembly Jigs & Assembly
Automotive & Robotics

Nylon SLS 3D Printing Services
Aerospace & Defense

Aerospace & Defense
Representation Model

Unmanned UAV 3D Printing
Aerospace & Defense

Canopies, Rubber Pads
Aerospace & Defence

Bio-Compatible Enclosures
Healthcare & Medical

Anatomical models for surgical planning
Healthcare & Medical

Bio Surgical guides
Healthcare & Medical

Industrial Grade Jigs & Fixture
Manufacturing & Tooling

Low Batch Production
Manufacturing & Tooling

Rapid Prototyping
Manufacturing & Tooling

Custom insoles and midsoles
Footwear

Toys & Action Figures 3D Printing
Consumer Products

Customized Home Decor
Consumer Products

Scale models of buildings
Architecture & Construction

Props, Sets and costumes
Film & Entertainment

EV Battery Management System
EV Automotive

EV Charging Stations
Interior and Exterior Components

EV Cell Holder 3D Printing
2W/4W Automotive

Assembly Jigs & Assembly
Automotive & Robotics

Nylon SLS 3D Printing Services
Aerospace & Defense

Aerospace & Defense
Representation Model

Unmanned UAV 3D Printing
Aerospace & Defense

Canopies, Rubber Pads
Aerospace & Defence

Bio-Compatible Enclosures
Healthcare & Medical

Anatomical models for surgical planning
Healthcare & Medical

Bio Surgical guides
Healthcare & Medical

Industrial Grade Jigs & Fixture
Manufacturing & Tooling

Low Batch Production
Manufacturing & Tooling

Rapid Prototyping
Manufacturing & Tooling

Custom insoles and midsoles
Footwear

Toys & Action Figures 3D Printing
Consumer Products

Customized Home Decor
Consumer Products

Scale models of buildings
Architecture & Construction

Props, Sets and costumes
Film & Entertainment
Outputs that speaks for itself
These works exemplify our expertise in delivering high-performance, customized 3D printed parts that meet industry standards delivered under tightest of timelines.
SLA-ABS
SLA-Clear
SLS-Nylon
FDM
Production-grade
Low-Batch
MJF
3D Scanning
Trusted by Industry Leaders Nationwide
From top brands to future icons, we help turn bold ideas into reality.
Meet Makenica®
3D Printing Since 2016
Founded by passionate makers, Makenica grew from firsthand manufacturing challenges into a mission—empowering the next generation of makers with the tools, support, and transparency we once needed.
How Makenica Works?
Transform your ideas into 3D printed parts—faster than ever. Upload your CAD file for instant quoting, rapid production, and doorstep delivery with end-to-end quality control.

1. Upload your CAD
One Click Login to upload your CAD files (STL, STP, OBJ)
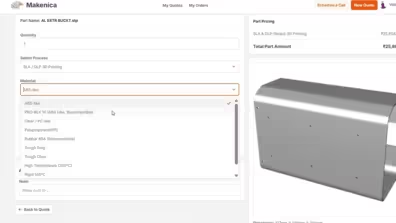
2. Get Instant Quotation
Get real-time instant pricing based on your CAD.

3. Start 3D Printing
Your parts move into production within hours.

4. Quality Control
Quality Control Team verifies accuracy & consistency.

5. Ready for Delivery
Shipped using top courier partners to ensure safe delivery.
Frequent questions & answers
Answers to questions about our 3d printing services and quotation platform.












































